That dreaded ‘404 Error – Page Not Found’ message – Broken links are not only annoying, they can lose you valuable sales, damage your reputation and hurt your SEO performance. Users seeing a 404 error are likely to move on to another site rather than persevere on yours.
If the link in your paid Ad campaign points to a missing page not only are you losing sales, but each failed hit is costing you. Broken links can also stop search engines from crawling your site and hence properly indexing it.
The problem typically happens when a page URL is changed and a user has the old link saved in their browser, a link on an affiliate or referral site has not be updated or Google is serving a cached page.
Alternately it could be an overlooked internal link from one or more pages on you own site.
Here I’ll show you how to build a couple of custom reports in Google Analytics, one to identify broken links from external sources and another for broken internal links which your developers need to fix.
Reporting on 404 Errors from External Sources
Here we are looking for cases where a user landed directly on a page that does not exist via a broken link. The first thing we need to do is see what the page title is for 404 errors on your web site. To do this browse to an invalid page on your site. I entered https://polkadotdata.com/nosuchpage. The page title should be displayed when you hover over the tab for the page in your browser.

In my case the page title is Page not found – Polka Dot Data. Now we can start building our report.
In Google Analytics go to Customization > Custom Reports and select New Custom Report.

Set the report title to something meaningful. I chose “404 Errors – External”.
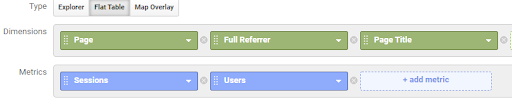
On the Report Tab set the type to report type to Flat Table.
Add Page, Full Referrer and Page Title as Dimensions
Add Sessions and Users as Metrics
Under Filters add a new filter to include only pages linked to from an external source

Add a second filter to only include pages where the title includes the text ‘not found’ – (substitute ‘not found’ with the 404 page title from your web site).

Save the report – Job Done!
When running the report remember to set a wide date range so you don’t miss any.
Reporting on 404 Errors from Internal Links
This report is very similar to the previous one, but intended for your developers so they can quickly fix any internal broken links.
Here we go..
On the Google Analytics Custom Reports page, locate the 404 Errors – External report we created in the previous section and make a copy by selecting Copy from the Action drop-down on the right.
Change the Title to 404 Errors – Internal
Change the Full Referrer Dimension to Previous Page Path
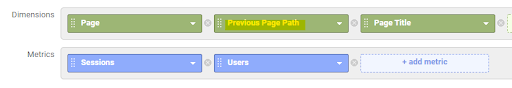
Change the first Filter to Exclude rather than Include pages linked to from an external source.

Save the report.
Again, make sure you use a wide date range when running the report so you don’t miss any.
In Summary…
In this blog post I showed how you can track down those pesky broken links on your web site using Custom reports.
If you are still unsure as to why you should be concerned about broken links and getting traffic to 404 pages, then check out this article by Site Improve which discusses the true cost of your sites broken links.
For the more technically minded, you can achieve similar results using Google Tag Manager to trigger an event each time someone hits a broken link.
Speak to our team about Google Analytics and Tag Manager training, and get the best from your Analytics data.
